The important basic parts of all cells are:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
CELL MEMBRANE
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. It is also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane. The cytoplasm and nucleus are enclosed within the cell membrane. It forms the wall-like structure between two cells as well as between the cell and its surroundings. It is the living part of the cell.
Structure:
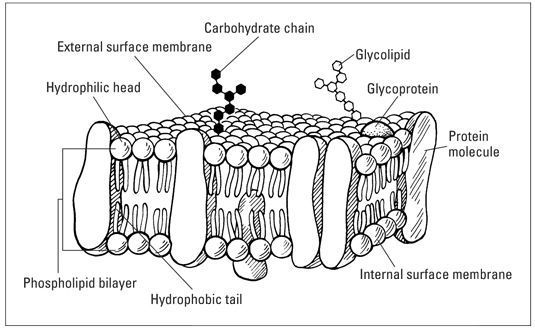
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, cholesterol and carbohydrate chains. This structure acts as a semi-permeable barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- In the phospholipid bilayer, the hydrophobic tails face inward and the hydrophilic heads face outwards, creating a barrier between the cell’s internal and the external environment.
- The two main types of proteins found in the plasma membrane are integral and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer. Peripheral proteins are attached to the membrane surface. These proteins help in transport, signaling and structural support.
- Carbohydrates attached to lipids and proteins form glycoproteins and glycolipids which help in cell recognition, adhesion, and signaling.
- Cholesterol helps to regulate its fluidity and stability.
Functions:
The main functions of the cell membrane are:
- It protects the cell and also gives shape to the cell.
- It regulates the entry and exit of substances in the cell. Thus, it is selectively permeable.
- It facilitates the communication with other cells via receptors.
- It regulates exchange of materials with its surroundings.
CYTOPLASM
The cytoplasm is the gel-like transparent substance which fills the cell between nucleus and cell membrane. Cytoplasm is a kind of chemical factory where new substances are built from materials taken into the cell, and energy is released and stored. It consists of cytosol (water + salts + proteins) and various structures of a cell, known as cell organelles. The most important organelle in the cytoplasm is nucleus. Other organelles include mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi bodies, etc. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colourless.
The cytoplasm and the nucleus together form protoplasm.
Functions:
The main functions of the cytoplasm are:
- Most of the chemical reactions of the cell take place in cytoplasm. Thus, it is a site of metabollic reactions.
- It provides a medium for the suspension of organelles and intracellular transport.
- Cytoplasm is responsible for giving a cell its shape.
NUCLEUS
The nucleus is often called the “brain” of the cell because it controls all cellular activities. Found in eukaryotic cells, it is a membrane-bound organelle that stores genetic material in the form of DNA. This DNA contains instructions for making proteins, which are essential for cell structure and function.
Surrounded by the nuclear envelope, the nucleus has pores that allow selective exchange of materials with the cytoplasm. Inside, the nucleolus plays a key role in producing ribosomes, the protein factories of the cell.
Structure:
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Its main parts include:
-
Nuclear Envelope – A double membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm and has pores for material exchange.
-
Nuclear Pores – Openings in the envelope that allow RNA and proteins to move in and out.
-
Nucleoplasm (Nuclear Sap) – A gel-like substance inside the nucleus that supports the chromatin and nucleolus.
-
Chromatin – DNA and associated proteins that carry genetic information; condenses into chromosomes during cell division.
-
Nucleolus – A dense region inside the nucleus responsible for making ribosomes.
Functions:
-
Stores Genetic Material – Houses DNA, which contains instructions for all cellular activities.
-
Controls Cell Activities – Regulates growth, metabolism, and protein synthesis.
-
Ribosome Production – The nucleolus inside the nucleus produces ribosomes.
-
Cell Division – Coordinates processes like mitosis and meiosis to ensure genetic material is passed to daughter cells.
-
Gene Expression – Controls which genes are turned on or off, affecting the cell’s functions
IMPORTANT FACTS
Cell Membrane
-
Also called the plasma membrane.
-
Made of a lipid bilayer with proteins.
-
Controls entry and exit of substances, maintaining homeostasis.
-
Provides protection and support to the cell.
-
Involved in cell communication and signaling.
Cytoplasm
-
The jelly-like fluid inside the cell, called cytosol, plus all organelles.
-
Supports and suspends cell organelles.
-
Site of many cellular reactions like glycolysis and protein synthesis.
-
Helps in transport of materials within the cell.
Nucleus
-
Known as the control center of the cell.
-
Stores DNA and regulates all cell activities.
-
Surrounded by a nuclear envelope with pores for material exchange.
-
Contains the nucleolus, which makes ribosomes.
-
Controls cell growth, reproduction, and gene expression.
